Drugs: What Parents Need to Know
Amphetamine
What it is: Amphetamines are very addictive stimulants that accelerate functions in the brain and body. They come in various forms including pills and tablets.
Also known as: speed, uppers, dexies, bennies
How it is used: Amphetamine are swallowed, smoked, snorted, or injected.
What it does: No matter how a person takes amphetamine, this drug hits with a fast high, making the user feel powerful, alert, and energized. These "uppers" pump up heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure, and can also cause sweating, shaking, headaches, sleeplessness, and blurred vision. Prolonged use may cause hallucinations and intense paranoia. Users who stop taking amphetamine experience withdrawal symptoms, such as aggression, anxiety, and strong cravings for the drugs.
Cocaine and Crack
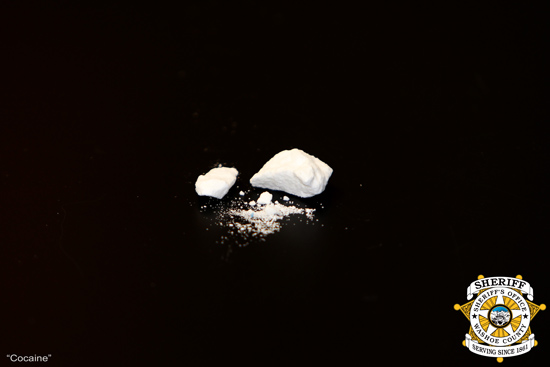
What it is: Cocaine usually is a white powder that comes from the dried leaves of the coca plant, which is frequently grown in South America. Crack cocaine is a form of the drug that gives a very quick, intense high, because it can be smoked. Crack is made by cooking cocaine powder with baking soda, then breaking it into small pieces called “rocks”. It got its name because it crackles when it is heated and smoked. Crack cocaine looks like white or tan pellets (sort of like gerbil or dry cat food). Both cocaine and crack are very addictive — and very, very dangerous.
Also known as: coke, rock, snow, blow, white, toot, nose candy, base, flake, powder, basa
How it is used: Cocaine is inhaled or snorted through the nose or injected into a vein. Crack is smoked in a pipe.
What it does: Cocaine is a stimulant, which means that it produces a fast, intense feeling of power and energy. Then it wears off (crack wears off very quickly) and the user feels depressed and nervous and craves more of the drug to feel good again. Cocaine is so addictive that someone can get hooked after trying it just once. Snorting cocaine can damage the septum between the nostrils, causing a hole in the middle of the nose. Cocaine makes the heart beat faster and blood pressure and body temperature go up. It also can make the heart beat abnormally. Cocaine is so dangerous that using it just once can cause a heart attack, stroke, or even death.
Depressants
What they are: Sedatives and other depressants calm nerves and relax muscles. Often they are bright-colored capsules or tablets that are legally available through a doctor for medical reasons, but can be illegally abused.
Also known as: downers, goofballs, barbs, blue devils, yellowjackets, ludes, benzos
How it is used: Depressants are typically swallowed.
What they do: When used as prescribed by a doctor, depressants can calm nerves, relax muscles, and treat insomnia or seizures. Larger or improperly used doses of depressant drugs can cause confusion, loss of coordination, low blood pressure, and slowed heart rate and breathing. Someone who takes them may have slurred speech and an inability to concentrate, and he or she may fall asleep at work or school. Depressants are addictive and withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, sleeplessness, and seizures. Depressant drugs are very dangerous if taken with alcohol, which also is a depressant, and certain other drugs. Very large doses of depressants can stop breathing and cause death.
Ecstasy


What it is: Ecstasy (3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine or MDMA) is a drug that is illegally made. Ecstasy is a stimulant drug that can cause hallucinations.. The drug is popular with teens and young adults who go to clubs, concerts, or "rave" parties. Users think the drug will make them feel good and enable them to keep going for days without rest. But people who use Ecstasy don't realize how dangerous this drug actually is. Ecstasy has become one of the most common illegal drugs sold on the streets. In the last few years, Ecstasy has sent many young people to emergency rooms because of its dangerous side effects. Ecstasy can kill.
Also known as: XTC, X, Adam, E, Roll, (Molly is another designer drug similar to Ecstasy)
How it is used: Ecstasy can be swallowed (pill or tablet) or snorted (powder).
What it does: Ecstasy is both a hallucinogenic and a stimulant drug. It makes users experience a rush of good feelings (a high) and makes feelings much more intense, whether they're good or bad. The drug's effects usually last up to 6 hours. Ecstasy increases heart rate and can cause dry mouth (dehydration), clenched teeth, blurred vision, chills, sweating, or nausea. It can make some users feel anxious, confused, and paranoid, like someone is trying to hurt them or is plotting against them. Ecstasy may cause damage to brain cells that are involved in thinking and memory. If a person takes Ecstasy, his or her body can dangerously overheat during dancing or other physical activities, which can lead to muscle breakdown, kidney, liver and heart damage, and even death. Taking the drug can cause seizures, brain swelling and permanent brain damage.
GHB
What it is: GHB (gamma hydroxybutyrate) is a depressant that is usually available in the form of a clear liquid. Like Ecstasy, GHB is popular with club-goers and those who go to "rave" parties, including teens and young adults. As a result, GHB is often referred to as the date rape drug.
Also known as: Liquid Ecstasy, G, Georgia homeboy
How it’s used: Swallowed (in liquid or powder form, which is mixed with water, or as tablets)
What it does: GHB has caused many young people to need emergency medical care. Because the liquid is odorless and colorless, GHB diluted in drinks is virtually undetectable and sometimes is slipped unknowingly into someone else's drinks. Side effects of GHB use include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and vision changes. People who take GHB may become unconscious (pass out), stop breathing, and go into a coma. GHB use can kill. Because both GHB and alcohol are depressants, mixing the two is very, very dangerous and can be deadly — even if someone has only taken low doses of the drug. Because of its serious effects, GHB has necessitated emergency medical care for many young people.
Heroin

What it is: Heroin belongs to a group of pain-relieving drugs called narcotics. Pure heroin has the consistency of white powder. Some heroin is also dark brown, while black tar heroin is either sticky or hard and looks like roofing tar. Although some narcotics like codeine and morphine are legal if prescribed for pain relief, heroin is an illegal narcotic in the United States, because it has dangerous side effects and is very addictive.
Also known as: horse, smack, big H, black tar, caballo (Spanish), junk, TNT
How it’s used: Heroin is usually injected or smoked. Purer forms of heroin are snorted.
What it does: Heroin provides a burst or rush of good feelings, and users feel "high" and relaxed. This may be followed by drowsiness and nausea. Many people who are addicted to heroin inject the drug into a vein with needles, and may inject the drug several times a day. Over time, the needle marks, or tracks, can become permanent scars. Often, heroin addicts will share needles, which can lead to infection with dangerous germs like hepatitis B or C or HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Heroin is a very addictive drug and many people find it extremely difficult to stop using it — even after using it for just the first or second time. Heroin users constantly crave their next dose. If heroin addicts suddenly try to stop using the drug or are unable to get another dose, they often develop withdrawal symptoms, like feelings of panic, sleeplessness, bad chills and sweats, muscle pain, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Taking an overdose of heroin can cause a person to stop breathing and die.
Inhalants
What they are: Inhalants are substances that are sniffed or huffed to give the user an immediate rush, or high. The substances inhaled are often common household products that contain volatile solvents, aerosols, or gases. People do not typically think of these products as drugs because they were never intended for that purpose. They include glues, paint thinners, dry cleaning fluids, gasoline, felt-tip marker fluid, hair spray, deodorants, and spray paint. Another common inhalant is known as a “whippet”, which is a whipped cream dispenser filled with nitrous oxide.
Also known as: whippets, poppers, snappers, rush, bolt, bullet
How they’re used: These are inhaled directly from the container (called sniffing, huffing or snorting), from a plastic bag (called bagging).
What they do: Many inhalants are central nervous system depressants and produce a quick feeling of being drunk — followed by sleepiness, staggering, dizziness, and confusion. Long-time users get headaches, nosebleeds, and sometimes lose their sense of smell. The harmful effects of inhalants can be irreversible. Inhalants decrease oxygen to the brain and can cause brain damage. Using an inhalant just one time can lead to life-threatening health problems, and even cause death.
LSD
What it is: LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) is a hallucinogenic drug. Hallucinogens change the way people sense the world around them. LSD is odorless, colorless, and tasteless. LSD is often added to absorbent paper, such as blotter paper, and divided into small decorated squares, with each square representing one dose.
Also known as: acid, sugar cubes, white lightning, dose, trips blotter
How it’s used: LSD comes in a variety of forms, but is virtually always taken orally. Today, LSD is most commonly found in the form of small squares of paper called blotter. The small piece of paper is placed on the tongue and the LSD is dissolved by saliva. Other forms of LSD include pills, gelatin sheets or shapes, liquid, sugar cubes, and powder.
What it does: LSD causes the senses of space, distance, and time to become altered. People say they "hear" colors or "see" sounds, and have strange feelings and strong emotions. Many users refer to an "acid trip" — when the effects don't let up and can last for up to 12 hours at a time. LSD also can cause "bad trips" — when users experience panic, confusion, sadness, and scary images. Bad reactions can occur with the first use and a user may have flashbacks later, experiencing the feelings of a bad trip even after the drug wears off. Because LSD also affects judgment and behavior, users might find themselves in a dangerous situation. Physical changes include increased heart rate and blood pressure, muscle twitches and shaking, dilated pupils, sweating, sleeplessness, and loss of appetite. LSD is very potent and very small amounts can produce undesirable effects.
Marijuana

What it is: Marijuana is the most widely used illegal drug in the United States. It is made from the shredded leaves, stems, seeds, and flowers of the Cannabis sativa plant. It looks like green, brown, or gray dried parsley. Marijuana is a mind-altering drug and is considered a hallucinogen if taken in large amounts.
Also known as: weed, grass, pot, chronic, joint, blunt, herb, cannabis, hash, Mary Jane
How it’s used: Marijuana is smoked as a hand-rolled cigarette (called a joint or a nail), in a pipe, or water pipe (also known as a bong); it is sometimes smoked after being placed inside of hollowed-out cigars called blunts; mixed into foods; or brewed as a tea.
What it does: Marijuana makes it hard to keep track of time and concentrate. Users have difficulty with memory and find it hard to solve problems and learn. Marijuana raises heart rate. Some people get red eyes or dry mouths or become sleepy or very hungry. The drug can also make some people paranoid (like someone is out to hurt them or is plotting against them). It can also sometimes cause hallucinations. Marijuana is as tough on the lungs as cigarettes — steady users suffer coughs, wheezing, frequent colds, and respiratory (airway and lung) infections, like bronchitis. Sometimes joints or blunts are laced with drugs like PCP (also called angel dust) or crack cocaine in addition to marijuana and can be very dangerous when smoked.
Methamphetamine (Meth)



What it is: Methamphetamine is a stimulant, a type of drug that gives someone the ability to stay awake and do continuous activity with less need for sleep. These drugs are produced as illicit pills, powders, or chunky crystals called ice. Ice, nicknamed crystal meth, is a popular drug, especially with young adults and for those who frequently go out to dance clubs and parties. Methamphetamine also is found in commercially manufactured tablets and capsules used to treat various medical conditions including narcolepsy, attention deficit disorder (ADD), and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Also known as: speed, uppers, meth, crystal meth, chalk, ice, glass, crank (especially when injected)
How it’s used: Methamphetamine is a white, odorless, bitter-tasting crystalline powder that easily dissolves in water or alcohol and is swallowed, snorted, smoked, or injected into a vein.
What it does: Oral methamphetamine ingestion tends to lack rushing, has less euphoric effects, and tends to cause far less of a feeling of wanting to do it again than the other methods. Smoking and injecting methamphetamine are associated with stronger, more euphoric effects and these are more associated with compulsive / addictive user patterns. People who abuse methamphetamines feel high and full of energy. They think the drug will allow their bodies to keep going and going. But methamphetamine is very damaging to the body and brain, especially with repeated use. Side effects include rapid breathing, an irregular heart rate, and increased blood pressure. Users also complain of sweating, headaches, blurred vision, dry mouth, hot flashes, and dizziness. Since the drug often decreases or even eliminates appetite, it has been used as a dangerous dieting strategy for people trying to lose weight quickly. Long-term use of methamphetamine can bring on brain damage that causes problems with memory and body movements, and can cause mood swings and violent behavior. When used in larger doses, methamphetamines can cause dangerously high body temperature, confusion, convulsions (uncontrollable jerking body movements), and even death.
Mushrooms (psilocybin)

What it is: Certain species of mushrooms indigenous to tropical and subtropical regions of South America, Mexico, and the United States contain the hallucinogenic substances psilocybin and psilocin. Distinguishing hallucinogenic mushrooms from poisonous and sometimes deadly ones can be very difficult and sometimes almost impossible, because many mushrooms have similar appearances.
Also known as: shrooms, Mushies, magic mushrooms, Psilocybe mushrooms
How it is used: Both the stems and caps are usually eaten fresh or dried. They can also be used to brew a tea or are added to food to mask their bitter flavor. Sometimes the mushroom material is ground and placed in capsules that are swallowed.
What it does: Consuming psilocybin mushrooms causes hallucinations and an inability to discern fantasy from reality. Panic reactions and psychosis also may occur, particularly if a user ingests a large dose. The effects are similar to LSD but may also include the feeling of euphoria and bodily excitement. They also take effect in a much shorter time (usually after about 30 minutes, peaking after about 3 hours) and last for a shorter time (usually between 4 and 9 hours). As with other hallucinogenic drugs 'bad trips' can also occur and may develop into a psychotic episode. A common danger is mistaking poisonous mushrooms for 'magic mushrooms'.
Nicotine
What it is: Nicotine is a highly addictive stimulant found in tobacco that is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream when smoked.
How it’s used: Nicotine is typically smoked in cigarettes or cigars. Some people put a pinch of tobacco (called chewing or smokeless tobacco) into their mouths and absorb nicotine through the lining of their mouths.
What it does: Nicotine is as addictive as heroin or cocaine, which makes it extremely difficult to quit. Those who start smoking before the age of 21 have the hardest time breaking the habit. Physical effects of nicotine use include rapid heartbeat, increased blood pressure, shortness of breath, and a greater likelihood of colds and flu. Smokers also have bad breath and yellowed teeth. Users have an increased risk for lung diseases like lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Chewing tobacco users also may suffer from cancers of the mouth and neck. Withdrawal symptoms of nicotine include anxiety, anger, restlessness, and insomnia.
